No products in the cart.
Bookkeeping
Book Value: Definition, Meaning, Formula, and Examples

If the market price for a share is higher than the BVPS, then the stock may be seen as overvalued. BVPS is typically calculated quarterly or annually, coinciding with the company’s financial reporting periods. In conclusion, the price-to-book value obtained suggests that the market could have undervalued the stock during that time. If we put the annual values into our price-to-book ratio calculator, we will get a PB ratio of 1.9, which is way above 1.07. An asset’s book value is calculated by subtracting depreciation from the purchase value of an asset. Depreciation is generally an estimate, and there are various methods for calculating depreciation.
- Often called shareholders equity, the “book value of equity” is an accrual accounting-based metric prepared for bookkeeping purposes and recorded on the balance sheet.
- If assets are being depreciated slower than the drop in market value, then the book value will be above the true value, creating a value trap for investors who only glance at the P/B ratio.
- However, tech companies that specialize in creating software don’t have an asset that is stored somewhere, and they don’t require expensive industrial equipment to produce their product.
- For example, if the BVPS is greater than the MVPS, the company’s stock market may be undervaluing a company’s stock.
- Rather than buying more of its own stock, a company can use profits to accumulate additional assets or reduce its current liabilities.
The Formula for Book Value Per Common Share Is:
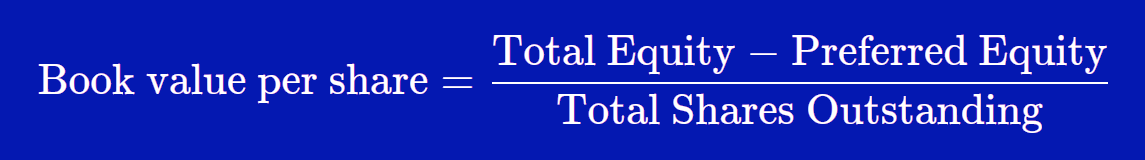
Breaking down the book value on a per-share may help investors decide whether they think the stock’s market value is overpriced or underpriced. If quality assets have been depreciated faster than the drop in their true market value, you’ve found a hidden value that may help hold up the stock price in the future. If assets are being depreciated slower chart of accounts and bookkeeping for a consulting business than the drop in market value, then the book value will be above the true value, creating a value trap for investors who only glance at the P/B ratio. Now, let’s say that Company B has $8 million in stockholders’ equity and 1,000,000 outstanding shares. Using the same share basis formula, we can calculate the book value per share of Company B.
Online Investments
This situation suggests a potential buying opportunity, as the market may be undervaluing the company’s actual worth. Another way to increase BVPS is for a company to repurchase common stock from shareholders. Assume XYZ repurchases 200,000 shares of stock, and 800,000 shares remain outstanding. The company generates $500,000 in earnings and uses $200,000 of the profits to buy assets, its common equity increases along with BVPS.
Book Value per Share Calculator
The term “book value” is derived from accounting lingo, where the accounting journal and ledger are known as a company’s books. To better understand book value per share, it helps to break down each aspect of the ratio. If a company is selling 15% below book value, but it takes several years for the price to catch up, then you might have been better off with a 5% bond. Remember, even if a company has a high book value per share, there’s no guarantee that it will be a successful investment. The book value per share is just one metric that you should look at when considering an investment. It’s important to remember that the book value per share is not the only metric that you should consider when making an investment decision.
What Is Book Value Per Common Share?
Also, since you’re working with common shares, you must subtract the preferred shareholder equity from the total equity. In the example from a moment ago, a company has $1,000,000 in equity and 1,000,000 shares outstanding. Now, let’s say that the company invests in a new piece of equipment that costs $500,000. The book value per share would still be $1 even though the company’s assets have increased in value. For example, let’s say that ABC Corporation has total equity of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding. This means that each share of stock would be worth $1 if the company got liquidated.
However, because assets would hypothetically sell at market value instead of historical asset values, this may not be an entirely accurate measurement. For companies seeking to increase their book value of equity per share (BVPS), profitable reinvestments can lead to more cash. In return, the accumulation of earnings could be used to reduce liabilities, which leads to higher book value of equity (and BVPS). Nevertheless, most companies with expectations to grow and produce profits in the future will have a book value of equity per share lower than their current publicly traded market share price. BVPS represents the accounting value of each share based on the company’s equity, while the market value per share is determined by the stock’s current trading price in the market. Should the company dissolve, the book value per common share indicates the dollar value remaining for common shareholders after all assets are liquidated and all creditors are paid.
The book value includes all of the equipment and property owned by the company, as well as any cash holdings or inventory on hand. It also accounts for all of the company’s liabilities, such as debt or tax burdens. To get the book value, you must subtract all those liabilities from the company’s total assets. The book value per share (BVPS) is a ratio that weighs stockholders’ total equity against the number of shares outstanding. In other words, this measures a company’s total assets, minus its total liabilities, on a per-share basis.
Companies that store inventory in a warehouse can count all of that inventory toward their book value. However, tech companies that specialize in creating software don’t have an asset that is stored somewhere, and they don’t require expensive industrial equipment to produce their product. They may generate sales with that software, but there isn’t a warehouse full of software code that investors can look at to gauge future sales.
Book value per share (BVPS) measures the book value of a firm on a per-share basis. BVPS is found by dividing equity available to common shareholders by the number of outstanding shares. The book value of a company is based on the amount of money that shareholders would get if liabilities were paid off and assets were liquidated.